Automation has changed the aspects of the business today. In addition, the opportunity of applying robotic automation in business processes has been gaining more attention as they challenge in a digital world, which requires faultless operations. With RPA Robotic Process Automation solution, businesses are automating knowledge-based, professional service processes that don't demand human interaction. Concurrently, it is serving as a fundamental activist to the conventional insight of labor arbitrage.
RPA is a recent development with origins firmly based on BPM. As our recent post, outlines the BPM Business Process Management , this blog will explore robotic process automation and its evolution in the business processes. So, let us understand, what is RPA?
RPA Definition
RPA is defined as an art of using software robots to interact with Software-as-a-Service applications and IT systems to automate the rule-based manual jobs associated with repetitive and transactional processes. The robot mimics the interactions of an employee with a system's user interface. The RPA services provide data security, enhanced business efficiency and effectiveness across various business applications without modifying available system and infrastructure. Robotic Process Automation can be termed as the breed of technology in the industries like Machine Learning, Automation Engineering and Artificial Intelligence. It can be considered as the low-risk process of performing business tasks in an automated manner than using the most valuable human resources on tasks that are repeated over the time. Further, RPA is for the non-technical businesspersons who are looking for the technology that do things for them rather than doing by themselves.
Manual Process Vs Robotic Process Automation
The following diagram depicts the manual process of providing the user with access to an application.
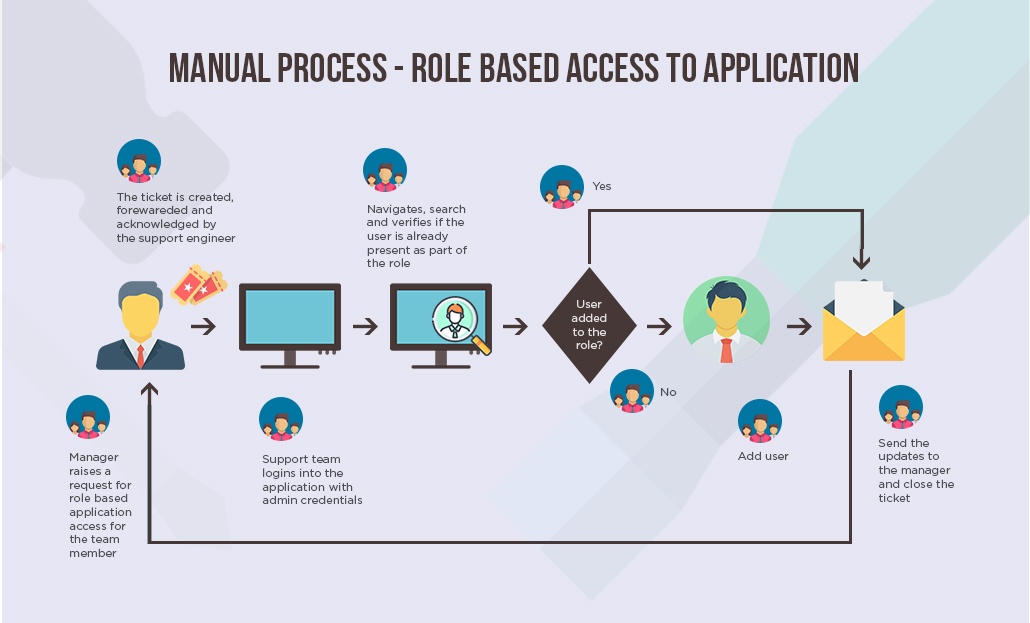
It is a labor-intensive process. In this approach, the employees are involved in the mundane routine task. As it highly relies on the action of the employee, it increases the chance of errors due to fatigue or lack of concentration.
In the contrast, implementing RPA tool in this process can benefit the support team to capture or record the routine activities performed and replay them.
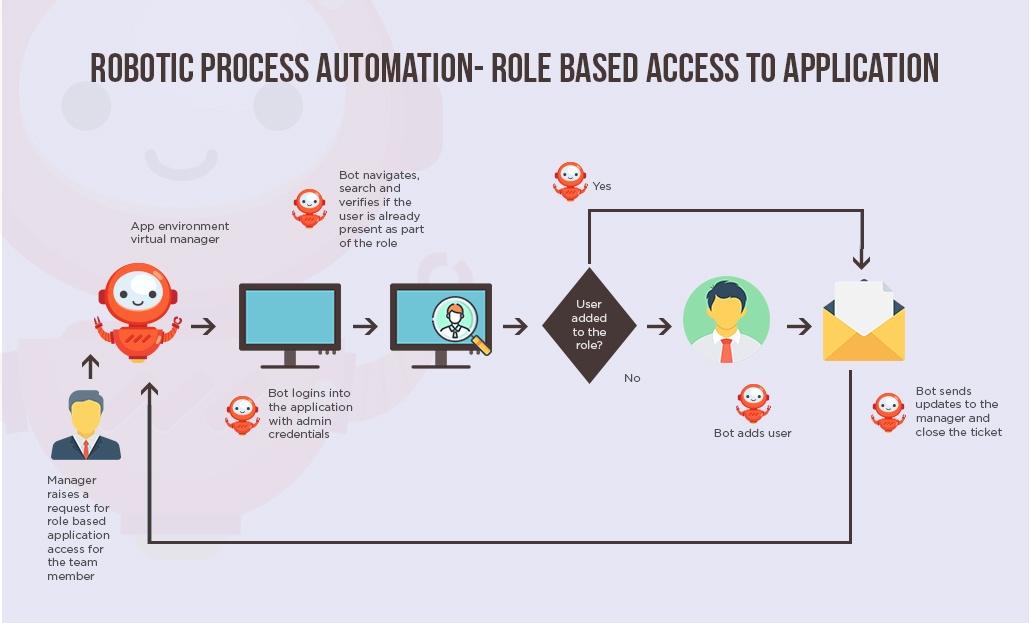
Here, the entire manual actions are recorded, scheduled and activated by a robot when required.
Robotic Automation (RA) Today
When it comes to robotics and automation, people usually think of it as robots or devices. However, RPA stands for virtual or invisible robots, which sits inside the systems, moving between various applications, checking, inputting, updating and processing more promptly that a human could. Therefore, RPA robotics is different from other direct types of automation. As like human user, RA interacts with different systems at the level of GUI or presentation layer. Hence, existing software systems can function together more efficiently; since, RA completes some tasks far faster and reliable than human do. This logical software tool shifts manual effort away from repetitive processing functions towards optimizing business processes. A major benefit is it connects existing system without re-engineering them. Alternately, it functions with various user interfaces like MS office documents, ERP systems and databases. Today's RPA systems are more flexible and accurate than humans are - they enhance compliance and are available 24/7.
Trends in the Evolution of RPA Market
RPA has evolved over recent years. Implementation of RPA software substantially enhances performance and minimizes the operation cost. Most processes in the organization are manual, repetitive and deterministic. Approximately 70% of those processes can be automated with software robots. In addition, processes, which require human judgment and involve greater complexity, can also be automated by combining software robots and human efforts. Organizations today begin to realize the evolution of automation and come forward to implement RPA in their businesses. This has led to a revolution in the RPA global market value. In 2020, the influence of robotic business process automation will become wider and the RPA software will be employed in more ways and across several sectors. It has been evidenced by the findings of the following reports:
- The Forrester research in 2017, found that robotic process automation market size, which was only 250 USD million in 2016, is predicted to reach 2.9 billion USD by 2021.
- Similarly, a report from Tractica stated that the global revenue in the RPA market would increase from 151 million USD in 2016 to more than 5.1 million USD by 2025.
- According to a recent report from Forrester Consulting on behalf of UiPath, a leading RPA vendor stated that the RPA market would exceed 1 billion USD by the end of 2018.
Therefore, based on these statistics, by the end of this year, around 75 % of all firms will have adopted the RPA technology.
To attain a competitive edge and continue relevant to the industry front-runners, most large enterprises have implemented RPA, and it has positively proved its utility in several scenarios. Robot software has shown substantial productivity advantages. To remain leading in this competition, companies are keen to implement RPA in their operations, which takes their business to the next level.
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation
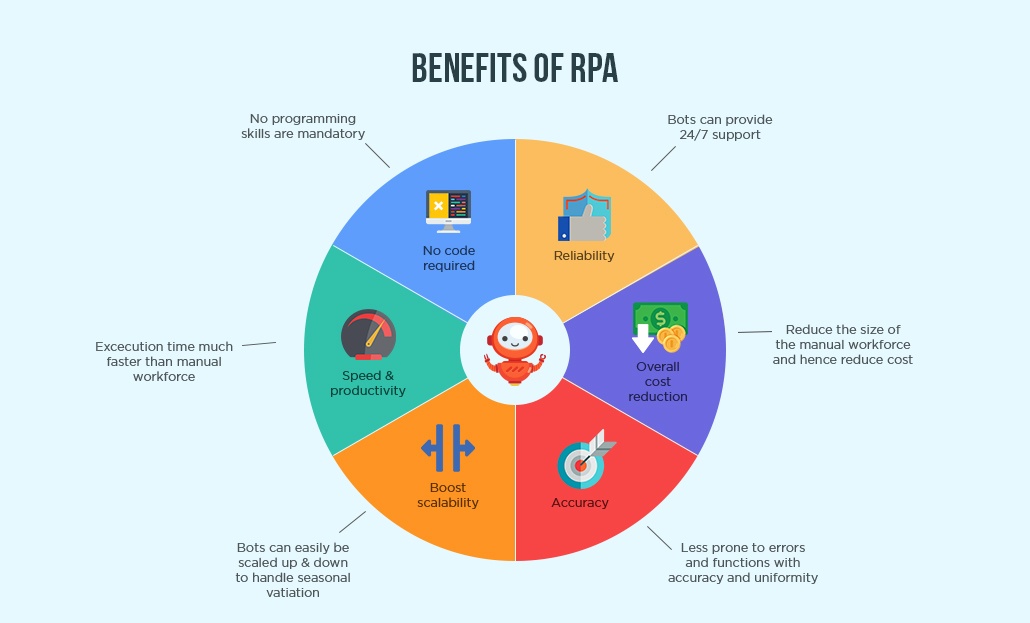
RPA boosts and scales up the business and performance of an enterprise by adapting and interpreting with the application for processing transactions, levering responses, manipulating data and interacting with other digital systems. Furthermore, with the power to self-correct and self-learn without human support, RPA implementation leads the extreme result. This technology can remove the high-cost demands by enabling process automation.
Procurement, Finance, and Accounting, FSI, Healthcare, Transport, IT/Telecommunication, Banking, Insurance, Manufacturing, and Production are some sectors that can benefit from RPA.
The following diagram depicts the benefits of adopting RPA in the enterprise:
Processes Suitable for RPA Adoption
All the usual repetitive, frequent, mundane, and high-volume tasks can benefit from RPA. As it is easy and quick to make an alteration, RPA is suited to tasks regularly adopt and change – particularly those that are complex and costly to re-engineer existing system within the short-term.
The followings are the most suitable processes for adoption:
- High volume of repetitive computer-based processes
- Process-documentation available in detail, rule-based transaction
- Low-level of exception processing
- Repetitive mouse and keyboard tasks, multiple sources of data input extraction and re-formatting
- Manual data entry between multiple non-integrated systems
- An operating environment that is impossible to change
For those considering RPA initiatives, it is vital to make sure that the initiative is a business-driven instead of technology-driven. Therefore, they should determine the right processes, which can leverage optimization and cost savings opportunities. The following section will assist to sort out the processes for adoption and to get real value from RPA.
Where can RPA Technology Implementation Add the Most Value?
Basic RPA generally focuses on simple processes like desktop consolidation, table population, task scheduling or CCP (Cut/Copy/Paste). On the other hand, advanced RPA can influence into more unstructured data using online digital assistants and chatbots. In addition, it is predicted that cognitive robotic process automation will be competent to deal with complex scenarios. Most commercially available applications today come under the basic RPA or advanced RPA. RPA delivers extreme benefits to enhance processes, which possess certain characteristics.
Tasks and data are the two important variables that aid to determine the RPA level required to attain extreme results. The following table explains the same with the reference of leonardo:
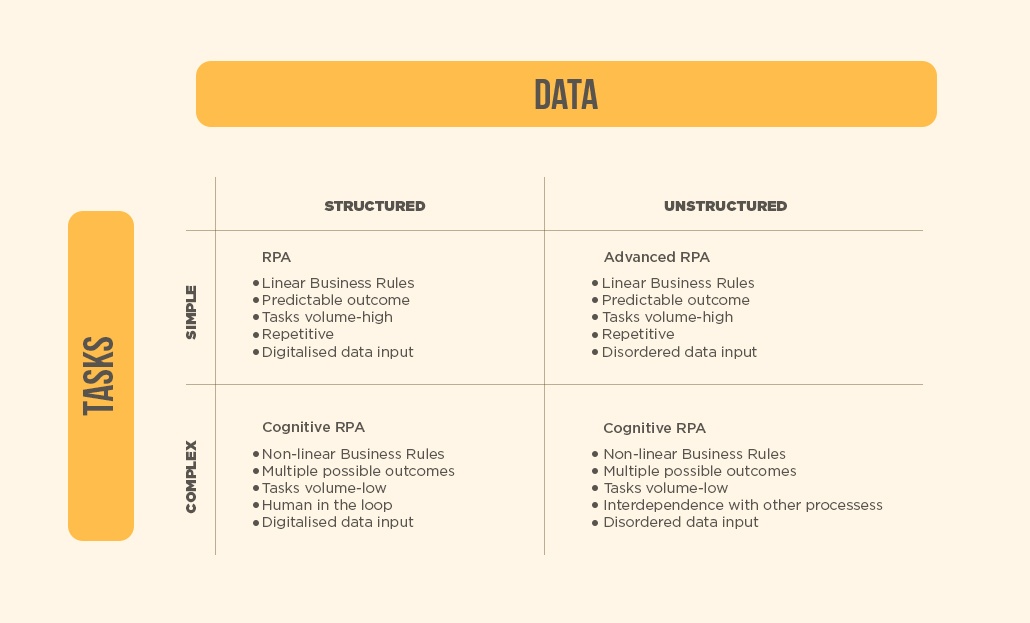
- Simple Tasks and Structured Data - The processes under this characteristic require ongoing human participation in large volumes. Undeniably, these processes are the great candidates for RPA implementation.
- Simple Tasks and Unstructured Data - Processes that demand unstructured and complex data management may not be the right candidate for basic RPA, but for the advanced RPA - the technology emerged to handle unstructured data. Practically, implementing RPA for this type of processes will sound viable only there are a high number of tasks being performed.
- Complex Tasks and Structured Data - Processes that require complex business decision and a large number of outcomes demand highly complex automation. Though we can implement RPA to collect the required information in the fast pace, there might be a requirement of human assistance to make the final decision. At this circumstance, businesses should make sure the cost of RPA implementation not outweighing the benefits.
- Complex Tasks and Unstructured Data - The processes under this combination require the human for effective handling and so, implementation of the RPA solution would be undeniably ineffective.
Robotic Process Automation Tools
RPA can be implemented with the support of various vendors. Some prominent players in the RPA market are:
- Uipath
- Automation Anywhere
- WorkFusion
- Pegasystems
- Softomotive
- EdgeVerve
- Kofax
- HelpSystems
- AntWorks
- NICE
- Blue prism
- Datamatics
- Jacada
- BlackLine
- Mozenda
- Verint
Conclusion
The RPA technology includes plenty of potential in shifting the way businesses operate. Undoubtedly, every business across the world will benefit from the competence of an automation system in the future. As long as industries are on the search for new solutions, a higher ROI and lower overhead, RPA will continue becoming more prevalent as well as sophisticated.



