Transform your Java microservices development with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud.
Blog Overview - Explore the significant impact that Spring Boot and Spring Cloud have on the development of microservices, mainly when used with Java. It underscores how these frameworks facilitate development by offering different features. Through a series of practical examples and real-world scenarios, the guide shows how Spring Boot and Spring Cloud empower Java developers in crafting microservices that are easy to deploy.
Spring Boot and Spring Cloud stand out for their comprehensive ecosystem, ease of use, and robust feature set. The transition from monolithic architecture to microservices has become a pivotal strategy for enhancing scalability, flexibility, and the overall agility of applications.
Know the unique aspects of building microservices with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud, understand their capabilities, use cases. Hire Java developers to craft resilient, scalable, and easily deployable microservices.
What are Microservices?
A Garner report states that around 74% of surveyed organizations use microservices. That shows a growing adoption rate, and many more will likely switch to it in the coming years.
Before diving into the specifics of Spring Boot and Spring Cloud, it's essential to grasp the microservices architecture. Microservices are an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled services, each implementing a specific business capability. This design principle enables individual service scalability, enhances fault isolation, and facilitates continuous deployment practices.
Netflix is a textbook example of implementing a microservices architecture effectively, maintaining its leadership position in the global entertainment sector. It supports millions of users worldwide through a complex yet efficient network of around 700 microservices, all hosted on Amazon Web Services cloud infrastructure. This intricate system of microservices forms the core of Netflix's operational framework, allowing for high levels of communication via Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). Such a setup permits the Netflix engineering team to perform updates or changes to any specific service independently without affecting the overall application's integrity. This decentralized approach significantly boosts the user experience by offering the agility and robustness needed for Netflix's service delivery.
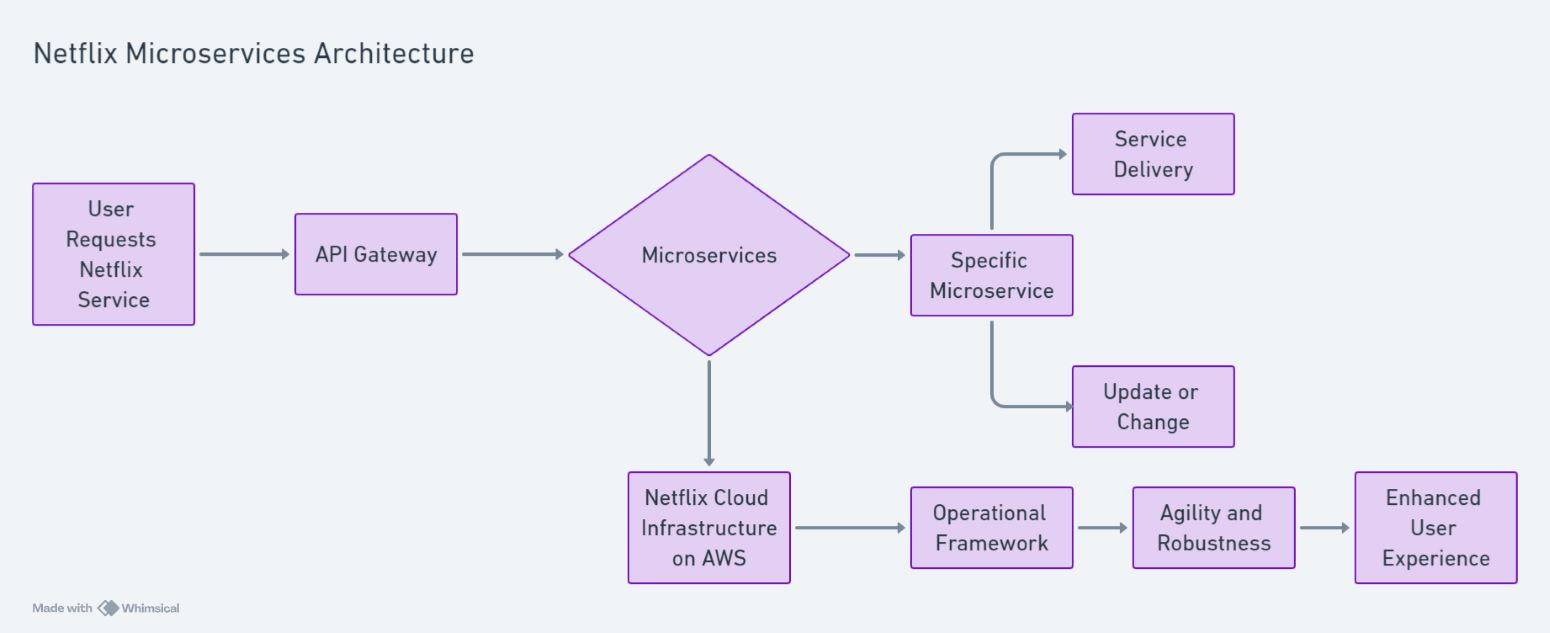
Java is pivotal in this architecture, as many microservices are developed using Java and the Spring Boot framework. Java offers a stable, scalable, and performance-oriented environment ideal for developing complex, distributed systems like those at Netflix. The language's rich ecosystem and the Spring framework's ability to simplify the development of microservices by providing essential features such as dependency injection, configuration management, and security contribute significantly to Netflix's operational efficiency. Moreover, Java's strong typing and JVM's (Java Virtual Machine) capability to run high-performance applications across different environments make it an excellent choice for building resilient services that can handle the demands of Netflix's massive global subscriber base. Netflix can efficiently manage its microservices architecture through Java and its frameworks, ensuring fast development cycles, scalability, and a seamless user experience.
The State of Java Microservices Market
As of 2024, the adoption of microservices architecture in Java-based applications has seen a remarkable surge, reflecting an industry-wide shift towards more scalable, flexible, and independently deployable services.
According to the latest International Data Corporation (IDC) 2024 report, over 65% of enterprise-level applications developed with Java now utilize microservices architectures. This significant increase from previous years highlights how organizations leverage Java's robust ecosystem, including frameworks like Spring Boot and Spring Cloud, to enhance their application's resilience, scalability, and overall performance.
Spring Boot: The Foundation of Microservices
Spring Boot represents a ground-breaking initiative within the Spring framework ecosystem, streamlining the crafting of new Spring applications by emphasizing simplicity and efficiency through its "convention over configuration" philosophy. This approach significantly reduces the initial setup and configuration effort, enabling Java developers to focus more on business logic than boilerplate code. With Spring Boot, the configuration of Java Beans, XML, and database transactions becomes much more flexible, and its autonomous nature eliminates the dependency on an external web server for application deployment.
Key Features of Spring Boot with Java
Auto-Configuration: Leveraging Java's robust ecosystem, Spring Boot intelligently configures applications based on the included dependencies, expediting the setup process and removing the guesswork from project initialization. Know which language is better for microservices Java vs. Python.
Standalone Capability: It harnesses Java's comprehensive library support to enable the development of standalone, self-contained Spring applications ready to run out-of-the-box, simplifying deployment and operations.
Opinionated Defaults: Spring Boot integrates well with Java, providing sensible default configurations that streamline development efforts. This includes predefined settings for logging, security measures, and database interactions, making it easier for Java developers to start with a strong foundation.
Spring Boot's Application in Java Projects
Microservices Architecture: Tailored for Java environments, Spring Boot facilitates the development of microservices by minimizing the complexity associated with service orchestration and configuration. Its auto-configuration feature is particularly beneficial for rapidly setting up and deploying microservices, enhancing agility and scalability. Know what is different in these two languages - Kotlin vs Java.
RESTful API Development: Java developers find Spring Boot incredibly valuable for creating RESTful services due to its straightforward approach and the extensive support provided by the Spring ecosystem. This makes it an excellent choice for developing backend services for web, mobile, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
Spring Boot and Java offer a powerful and efficient way to develop applications, particularly suited for modern microservices architectures and RESTful service creation. Its automation, self-contained application capabilities, and preset configurations significantly reduce development time and effort, enabling Java developers to deliver high-quality, scalable, and resilient applications more swiftly with Java development services.
Spring Cloud: Building Cloud-Native Microservices
Spring Cloud is an advanced toolkit within the Spring ecosystem, specifically designed to address the complexities of building and managing distributed systems, such as microservices, in cloud-native environments. Building upon the foundations laid by Spring Boot, Spring Cloud enhances and extends its capabilities towards the specialized demands of cloud development by introducing a range of tools and services tailored to common distributed system patterns like configuration management, service discovery, and fault tolerance.
Core Features of Spring Cloud with Java
With seamless distributed configuration Spring Cloud Config offers an efficient way to handle application settings across various environments, streamlining the deployment and operational processes for Java-based microservices.
It offers enhanced scalability and resilience. The framework's service discovery and load-balancing capabilities enable Java applications to scale and maintain performance, even under dynamically fluctuating loads.
With efficient API gateway integration with Spring Cloud gateway, Java developers can more easily implement gateways for routing and securing requests to and from a constellation of microservices, thereby improving the architecture's overall efficiency and security.
- Service Discovery: Utilizing Java's network communication capabilities, Spring Cloud incorporates service discovery mechanisms, notably through Netflix Eureka. This allows Java-based microservices to automatically detect and communicate with each other, removing the need for hardcoded addresses.
- Unified Configuration Management: Spring Cloud Config leverages Java's environment and property management features to centralize and manage configurations for all services, regardless of the deployment environment. This simplification is crucial for maintaining consistency and ease of management across numerous services.
- Fault Tolerance with Circuit Breakers: Implementing the circuit breaker pattern, particularly with Netflix Hystrix, Spring Cloud provides Java applications with a way to prevent system failure in the face of errors or excessive latency in individual microservices.
Application Scenarios for Java and Spring Cloud
- Web Applications:
Recognized for building web applications with efficiency. Supports embedded servers like Tomcat, Jetty, or Undertow for standalone, production-grade applications. Auto-configuration capabilities and Spring MVC for RESTful web services and dynamic websites. Supports templates like Thymeleaf for straightforward MVC application development.
- Microservices:
Ideal for developing lightweight, independently deployable services. Compatible with Spring Cloud for building distributed systems patterns (configuration management, service discovery, circuit breakers). Promotes scalability, resilience, and modularity, fitting for organizations transitioning to microservices.
- Cloud-Native Applications:
Aligns with cloud-native development principles for creating resilient, manageable, and observable applications. Actuator module provides insights into application health, metrics, and audit events. Seamless integration with containerization tools like Docker and Kubernetes for streamlined cloud deployment.
- Enterprise Applications:
Caters to complex requirements of enterprise applications. Integrates seamlessly with Spring Security, Spring Data, and Spring Batch. Suitable for developing secure, transactional, and data-intensive applications, managing security protocols, transactions, and data processing.
- IoT and Big Data Applications:
Suitable for the IoT and big data fields for developing lightweight, high-performance applications. Serves as the backbone for IoT devices' data collection and processing layers. Compatible with big data processing tools like Apache Kafka and Spring Data for real-time data processing and analytics.
Practical Insights on Spring Boot and Spring Cloud in Java Environments
Consider an e-commerce platform built with Java, comprising distinct services like user management, product catalog, and order management. Spring Boot is instrumental in developing these services, enabling quick, straightforward deployment. Spring Cloud elevates this setup by facilitating dynamic service interaction and efficient configuration management across the platform while providing resilience through its circuit breaker mechanism.
Addressing Challenges
Despite the advantages Spring Boot and Spring Cloud bring to Java-based microservices development, challenges such as the intricacies of inter-service communication and external configuration management persist. However, these challenges can be effectively mitigated by leveraging the comprehensive suite of tools offered by Spring Cloud, alongside adopting microservices best practices like domain-driven design and embracing continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) strategies.
Integrating Java with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud offers a powerful synergy for developing and managing robust, scalable, and resilient microservices architectures, simplifying the complexities associated with cloud-native application development.
A Comparison - Java with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Below is a comparison table that outlines the key differences and focuses of Spring Boot with Java and Spring Cloud with Java, highlighting their unique features, primary use cases, and how they contribute to the development and management of microservices architectures.
|
Feature/Aspect |
Spring Boot with Java |
Spring Cloud with Java |
|
Core Purpose |
Simplifies the development of Spring-based applications, making setup and configuration easier. |
Enhances Spring Boot applications for cloud-native microservices with distributed system support. |
|
Key Features |
- Auto-Configuration Standalone Applications Opinionated Defaults |
- Service Discovery (e.g., Netflix Eureka)- Configuration Management (Spring Cloud Config)- Circuit Breaker (Netflix Hystrix) |
|
Primary Use Cases |
- Rapid development and deployment of microservices- Creating RESTful services |
- Managing configurations across multiple environments- Dynamic scaling and resilience of services- Implementing API gateways |
|
Development Focus |
Focused on the rapid development and ease of application setup. |
Focused on solving the complexity of operating microservices in cloud environments. |
|
Operational Complexity |
Lower complexity, aimed at getting applications running quickly and efficiently. |
Higher complexity, with tools to address the intricacies of distributed systems. |
|
Scalability & Resilience |
Provides the foundation for building scalable and resilient applications but focuses more on individual service functionality. |
Directly addresses scalability and resilience through patterns like service discovery and circuit breakers. |
|
Configuration Management |
Offers essential configuration management but primarily through application properties and profiles. |
Offers advanced, centralized configuration management suitable for multiple environments and services. |
|
Service Discovery |
Does not inherently provide service discovery; it relies on integrating with external tools or Spring Cloud. |
An integral part of the framework, facilitating seamless service interaction and discovery. |
|
Deployment Environment |
Ideal for both cloud and non-cloud environments, emphasizing simplification and speed. |
Tailored for cloud-native applications, addressing specific challenges of cloud deployments. |
This comparison highlights that while Spring Boot with Java focuses on simplifying the development process with rapid setup and minimal configuration, Spring Cloud with Java builds upon this foundation to address the challenges of building and managing distributed cloud-native applications. Together, they offer a comprehensive suite of tools for developing robust microservices architectures, each serving distinct but complementary roles in the application development lifecycle.
Leveraging Java Expertise in Microservices Architecture:
Hiring Java developers for building microservices with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud is a strategic decision that taps into the rich ecosystem and robust capabilities Java offers for such architectures. Java development services are critical in this context because they bring a level of Java expertise essential for harnessing the full potential of Spring Boot and Spring Cloud in creating highly scalable, resilient microservices.
This expertise ensures that the inherent complexities of java microservices architecture are managed effectively, leveraging Java's strong typing, memory management, and vast library ecosystem. Moreover, Java development services come with a deep understanding of how to best utilize Spring's suite of tools, facilitating seamless integration, rapid development, and maintenance of microservices. This Java expertise is indispensable for businesses aiming to develop sophisticated, high-performing microservice applications that stand the test of time and scale.
Conclusion
Spring Boot and Spring Cloud offer a robust framework for building and managing microservices, providing Java developers with a comprehensive toolkit to create scalable, resilient, and cloud-native applications. Their unique aspects, including auto-configuration, standalone capability, service discovery, and configuration management, cater to various use cases, from building individual microservices to managing complex, distributed systems. By harnessing the power of Spring Boot and Spring Cloud, Java development services can significantly reduce development time and effort, paving the way for more innovative and flexible applications in the cloud era. As the microservices architecture continues to evolve, the Spring ecosystem remains at the forefront, continually adapting and introducing new features to meet the demands of modern application development.
Author







