Clouds are everywhere and it influences everyday life! From your emails, social media, shopping apps to banking transactions all use the cloud one way or another. Approximately one half of the US Govt. agencies are using cloud and 60% of American IT decision-makers trust that the cloud is safe.
So what is cloud computing and how the cloud computing architecture works? Read this blog to know everything about cloud computing architecture.
You can explore more about Salesforce Cloud.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is on-demand accessibility of computer resources. In simpler terms, cloud computing refers to the idea of using a network of remote servers on the Internet to accumulate, manage, and route the data. Delivering any computing service on the Internet is cloud computing. These cloud computing services can be storage, server, database, software, networking, intelligence, and analytics. When we say on-demand accessibility, it nurtures the idea of only paying for the services you are using.
Businesses are adopting cloud computing for its multi-fold benefits like minimizing capital expense, on-demand self-services, global scalability, optimum performance, security, high productivity, and reliability. Let’s understand the core areas of cloud computing with a diagram.
Cloud computing features three levels of connectivity including the cloud, network-devices like router& switches, and end-user.
The cloud comprises resources like virtual desktop, software platform, servers, applications, and data storage. They process data through routers and switches.
And the end-user can access the information from any device.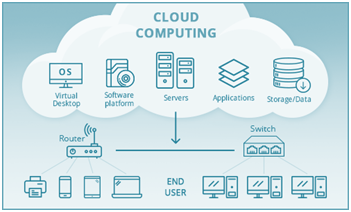
Image source: toolbox.com
Broad Divisions of Cloud Computing Architecture
The cloud computing architecture comprises two fundamental components, i.e. frontend and backend. Frontend works as a client in such architecture and communicates with the backend via a network or internet. In the cloud computing architecture, the client-side or frontend is visible to the end-user. The frontend sends queries to the backend via the middleware.
The backend protects the data and respond to the queries asked by the frontend. The backend is a bigger part of the whole cloud computing architecture as shown below: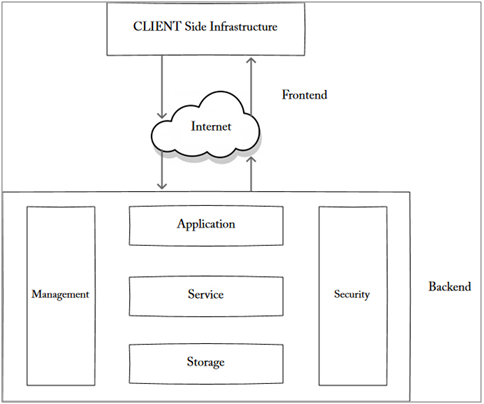
Image source: w3schools.in
This whole cloud service model is called Backend-as-a-service or BaaS.
In a business setting, finding out the suitable software & hardware components that create the whole cloud environment is important. While you can choose the hardware as off-the-shelf pieces and can choose the software as per business requirement & budget. The leading cloud service providers offer the whole package of paired hardware & software.
If you are planning to migrate to the Cloud, selecting appropriate cloud software architecture for your business is one of the most important business decisions. Ineffective cloud computing architecture planning can lead you to low cost-effectiveness zero-scalability. The suitable cloud computing architecture allows you to take care of all the software & hardware components.
Components of Cloud Computing Architecture
The fundamental components of the cloud computing architecture are:
- Front-end platform
- Back-end platform
- Cloud-based delivery
Besides the front-end and back-end platforms, cloud-based delivery allows transmitting information via various cloud infrastructures such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
What is Front End Cloud Architecture?
The front end infrastructure includes everything that the end-user interacts with. It is the broader assimilation of various sub-components that together offer the user interface. And it forms an essential part of how the end-user connects to the cloud computing infrastructure. The front-end cloud infrastructure includes components like local networks, web browsers, and web applications.
The main front-end cloud components are described below:
- User Interface: The user interface refers to all the things that end-user access to send requests or perform any task on the Cloud. Some of the popular cloud-based user interfaces are Google Doc, Gmail, etc.
- Software: The software architecture in the front end is the software that runs on the user’s end. Frontend software architecture primarily comprises client-side applications or browsers.
- Client Device or Network: Being a crucial part of the frontend architecture, Client Device or Network refers to the hardware at the end user’s side. It can be any input device or PC. In cloud computing, the client-side device doesn’t require extraordinary ability to process the heavy load. The cloud can take the entire heavy load and processes the same.
What is Back End Cloud Architecture?
The backend architecture in the cloud empowers the frontend architecture. It comprises hardware & storage and they are located on a remote server. The cloud service provider controls and handles this backend cloud architecture.
Ideal backend cloud architecture always should be robust as it holds the whole infrastructure on the cloud. The prime components of backend cloud architecture are:
- Application: The Application is a substantial part of the backend architecture. It refers to the user interface that the backend offers to the end-user to send queries. This layer of the backend takes care of the client’s requests and requirements.
- Service: This is a magical area of the backend cloud architecture. It adds utility to the entire backend architecture. The service handles every task that runs on the cloud computing system. Some of the cloud services are application development environment, storage, and web services. Besides, service can execute a wide array of tasks on the cloud runtime.
- Cloud Runtime: The term ‘Cloud Runtime’ is the concept where the services run. It’s like a cloud operating system where technology like virtualization is used. Virtualization as a key technology on the cloud which allows multiple runtimes on the same server. For instance, virtualization is a way via which we can create a base of software. In simple words, it’s the virtual representation of apps, servers, storage as well as networks. When we create runtimes with the support of virtualization software, they are called as Hypervisors. Some of the leading hypervisors are Oracle Virtual Box, Oracle VM for x86, VMWare Fusion, etc.
- Storage: Storage in the cloud is where the data resides of a cloud application. The data storage varies as per different cloud service provides. However, all of them have a common dedicated segment for cloud storage. Some of the examples of storage are solid-state drives, hard drives, Intel Optane DC Persistent storage, etc. The hard drives in the server bays form storage in the cloud backend architecture. And especially in a cloud computing system, the software partitions the drives as per the needs of the OS in the cloud to run myriad services.
- Infrastructure: The engine that steers all the cloud software services is called infrastructure. It includes CPU, Motherboard, Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), network cards, accelerator cards, etc. The infrastructure models always depend on the workloads of the clients.
- Management: The management software allocates specific resources to specific tasks and responsible for the flawless functioning of any cloud environment. In technical terms, management is the ‘middleware’ and it coordinates between the frontend and backend architecture in a cloud computing system.
- Security: Security is an integral and critical part of any cloud computing infrastructure. We create security infrastructure by keeping the debugging process in mind. In case of any issue, debugging should be easy. Regular storage backup is the first step to ensure security in a cloud computing system. And virtual firewalls are other crucial elements of the cloud security infrastructure.
Cloud-based Delivery
In layman’s language, cloud-based delivery is anything we are offering to the end-users from the cloud via some software, infrastructure, and platforms. We can deliver cloud computing services via the below-mentioned models:
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Offering cloud computing services via licensed software or subscription. In this delivery model, the end-users don’t need to buy or install any hardware at their locations.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): This model offers a platform that allows the end-users to develop, run as well as manage applications on the cloud. In PaaS, a third-party service provider facilitates hardware & software tools.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This model facilitates computer hardware like networking technology, servers, storage, and data center space as a service. It also includes the delivery of virtualization technology and operating system.
Cloud Service Network
We can offer cloud computing services via private and public networks. Besides, we can also use the end user’s network and offer the services via the intranet. Or else, we can combine both public and private networks to provide the services.
In a cloud computing service network, the end-user can own a datacenter or they can use the service provider’s datacenter to enable on-demand access of various resources like server, storage, network, application, and services.
Cloud service in Clarion
At Clarion, We support SMEs to build cloud applications. Our cloud experts are well-versed in modifying cloud setup and migrating application to the cloud. Our best-in-class cloud services include:
- Application migration to the cloud
- DevOps
- Content Management System (CMS)
- Cloud Migration
- Application development on the cloud
Conclusion
When we talk about cloud computing architecture, security is an undeniable factor that plays a crucial role. The EU Data Protection Policy viz. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) became mandatory from May 2018 that allows the users to right to request for data from any organization storing about them. And most importantly, the data can be forgotten if the users wish for it. The GDPR redefines the data management roles of the key leaders from CIOs to CMOs.




