How does your digital product's speed and reliability stay intact with the help of Performance Testing? Know the highlighted benefits and strategies for achieving optimal performance of your software.
Fast development of the digital environment brings high importance to strong testing and quality assurance (QA). Increasing demands regarding reliability, security, and user satisfaction require businesses to implement comprehensive testing and QA services. Thus, this blog reveals some details about testing and QA processes in their essential roles within software development. From making sure a user is not exposed to vulnerabilities due to incomplete experiences, we show how these practices can increase product quality as well as promote innovation and create a competitive advantage in Digital Marketplaces.
What is Performance Testing?
Performance testing has always been a crucial activity in the software development life cycle to confirm whether the applications indeed meet the desired performance criteria. Obviously, this process is fraught with various challenges. So let’s dive into common hurdles that one faces while performing performance testing in the blog. We will come up with strategic solutions to effectively sail over these issues and have your applications really running and roaring.
Boost your projects with precision and excellence. Hire testing engineers so you can redefine software quality now!
Why use Performance Testing?
Performance testing is the testing of performance in terms of response and stability of a system under some workload. It does not involve bug hunting but rather identifying bottlenecks and tuning a software application for speed, scalability, and reliability. This has become testing of major interest as it will be able to throw some light on the behavior of applications under conditions of stress and whether they are capable of handling large traffic and data processing.
To explain how often performance testing is used and what major challenges it helps to overcome, let us create a hypothetical graph. Two main components will be included in it.
Let us proceed with creating a hypothetical graph that covers these aspects.
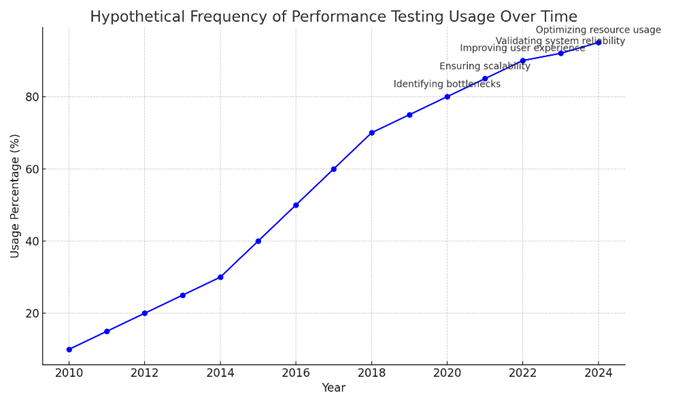
The hypothetical chart above shows the frequency by percentage usage of performance testing between 2010 and 2024, such increasing percentage usage reflects increased awareness as well as adoption of performance testing in software development projects. This proves how important performance testing has become when it comes to ensuring quality software and satisfied users.
Key Challenges That Performance Testing Can Solve:
-
Identify bottlenecks: Performance testing will help spot those areas where the system may degrade under load, and developers can tune all such areas.
-
Prove scalability: This assures that the system is capable of handling increasing work, i.e., workload, thus helping in planning future growth.
-
Better user experience: A fast responding application that stays stable in different conditions will always ensure a good user experience.
-
Validating system reliability: In stress and long runs, it's akin to checking how well the systems can sustain varied scenarios of operation for extended periods of time.
-
Resource optimization: Since performance testing can reveal any wastage of resources, hardware, and software can be used more efficiently.
Our cutting-edge mobile app testing tools boost your app's performance and user satisfaction. Try it now for seamless, bug-free applications!
Common Challenges of Performance Testing
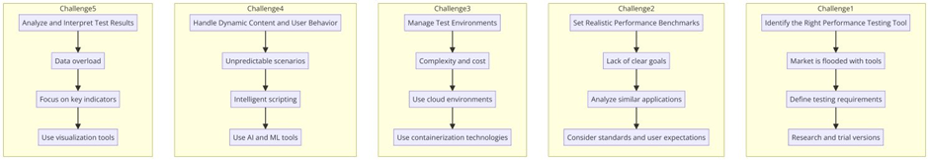
1. Identifying the Right Performance Testing Tool
Challenge: The market offers a great number of tools related to performance testing, and each tool includes some specific features, advantages, and disadvantages. If the tool is chosen incorrectly, then the testing might not be appropriate as well, and it may result in increased costs and wasted efforts.
Solution: Begin by articulating your testing needs. State the technologies running in your application, mention the load expected on it, and specify particular metrics to be measured. Do some tool research and comparison based on these criteria. Try their trial versions to see which one fits your requirements before making a decision.
2. Setting Realistic Performance Benchmarks
Challenge: If there is no clear, achievable performance goal, testing may be perceived as a never-ending, purposeless activity. It will be very difficult to convince oneself that the system is performing well enough.
Solution: Realistic performance benchmarks are obtained from the performance of similar applications and through industry standards, while also taking into consideration user expectations. They have to be specific and measurable and achievable and relevant and time-bound.
3. Managing Test Environments
Challenge: Performance testing requires an environment as robust as production. Setting up such an environment is not just complex but also time-consuming and expensive.
Solution: Use a cloud-based testing environment that will be scaled to mimic the production environments. In this setup, the cost and time for setting up the environment are minimized while different conditions can be tested. Additionally, containerization technologies such as Docker may be used so that application dependencies and configurations are easy to replicate.
4. Handling Dynamic Content and User Behavior
Challenge: The modern application very typically includes dynamic content, and at times, it becomes difficult to script and predict all variations that may take place based on different user interactions.
Solution: Intelligent scripting of the test and data parameterization will mimic actual user behaviors and data variations. Tools enabled with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities will serve to auto-adjust the test scripts according to patterns in user behavior.
5. Analyzing and Interpreting Test Results
Challenge: Test results often yield massive data over a wide range of metrics. To turn that into actionable insight is daunting.
Solution: Keep your eyes on response time, throughput, and error rates- they are the KPIs that directly impact the user experience and most probably your business goals too. Use visuals to simplify analysis and highlight the areas that demand keen attention.
Boost your software using our leading Testing & QA Services. Make it secure. Improve and create new possibilities with us now!
Implementing Solutions in Performance Testing
1. Automate Where Possible
Begin automation wherever it is possible. Performance testing can only become faster and more reliable if there is supporting automation, such as automated test environment setup, test case execution, and result collection- hence reduced time consumption and minimized manual errors. Performance testing tools should be integrated within CI/CD pipelines for proper automatic testing from the very first stages of development.
2. Prioritize Based on Risk and Impact
No part of the application bears equal weight on performance. Let critical components that can mar performance be known and prioritized in testing thereof. This approach, based on risk, ensures efforts are directed to those particular sections of the application that are most critical.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Performance testing is a continuous process that starts from development and goes all the way through. In production, set up continuous monitoring to catch performance problems as they happen in real time. Take what you learn from the monitoring to keep tuning and improving performance.
4. Foster Collaboration Among Teams
Practical performance testing requires the collaboration of developers, testers, and operations teams. It encourages open communication between all stakeholders by sharing the goals and results of performance testing. Only through such cooperation can every stage in the lifecycle be inculcated with an understanding of performance.
Types of Performance Testing
-
-
Load Testing: Performance is one of the most important components of software testing that determines how well the application can work under a certain load. Bottlenecks need to be identified for elimination to achieve enhanced performance of any software application. Some tests are carried out based on different concerns related to its performance, and they are described here.
-
Stress Testing: Load testing is basically a test of the ability of the application to perform under expected user loads. This is essentially to be able to fish out performance bottlenecks before going live with the software application.
-
Endurance Testing: Stress testing basically means throwing some insane workloads at an application just to see how well it deals with heavy traffic or data processing. Finding out where the break-point of an application lies is what this drilling down into.
-
Spike Testing: It throws at the software huge sudden spikes in the load that users generate. It helps ascertain if the application will continue to function when there is a huge change in user load.
-
Volume Testing: In this, it throws a large volume of data at the system to judge its behavior and performance against different volumes of databases. This will reflect the effect that changing data volumes has on performance.
-
Scalability Testing: Scalability testing is basically meant to find out at what point the application's performance starts degrading or how well the application is able to scale with increasing loads. This assists in planning the addition of capacity to your software system.
-
Concurrency Testing: Concurrency testing basically checks how well the system performs when multiple users perform the same action concurrently. It becomes very important for applications where systems expect simultaneous access by many users.
-
Configuration Testing: Configuration testing does not test the application for its performance regarding load, but checks and ensures that various configurations provide the intended optimal level of performance. This includes hardware, software, and network setups.
-
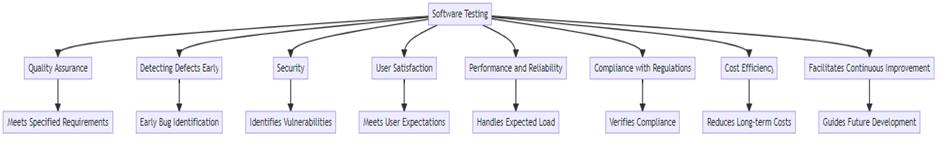
Importance of Software Testing
Software testing forms an integral part of the software development process in playing several vital roles in ensuring the quality, reliability, and performance parameters of a software product. The importance of software testing may be gauged from the following points:
-
Quality Assurance: Quality Assurance Software testing is the process of making sure that the product is as per the requirements specified and is working properly. This will enable one to identify variance between the actual and expected results, thus ensuring the attainment of quality objectives for a software product.
-
Detecting Early Defects: By identifying bugs and issues at an early stage of the development cycle, software testing can save time and resources. Early detection of defects means they can be fixed before they escalate into more significant problems, reducing the overall development cost.
-
Security: Testing is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and security flaws within the software. With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, ensuring the security of software products is paramount. Security testing helps protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access, thus maintaining the trust of users.
-
User Satisfaction: A well-tested software product is more likely to meet user expectations and needs. Testing ensures that the software is user-friendly, performs efficiently, and is free from critical bugs that could frustrate users. Satisfied users are more likely to continue using the product and recommend it to others.
-
Performance and Reliability: Testing relates to the degree to which software can bear the expected load and run at the speed level users wish. Reliability testing means measuring how long, under specified conditions, software can perform its functions. In turn, all this transforms into keeping a good user experience, particularly when talking about applications that require high demand.
-
Compliance with Regulations: Most software products are supposed to comply with standards and regulations in many industries through testing. This will verify compliance with the fulfillment of legal and safety standards by the software, especially when it is being used within healthcare, financial, or aviation transactions.
-
Cost Efficiency: Testing is less costly in comparison with the expenditure that needs to be borne if bugs are fixed post-deployment. The damage that would be inflicted on the brand due to bugs surfacing during usage would be more than any investments in testing.
-
Enables Continuous Improvement: Software testing throws back information on performance and usability aspects to developers for their further development endeavors. This feedback mechanism forms a vital component of continuous improvement and innovation.
Conclusion
Performance testing is naturally considered to be mandatory because in the fast digital world of today, users want quick responses from applications. Challenges regarding a test and their solutions that will be discussed here will help organizations maintain their applications at the optimum level of performance corresponding to user expectations. The Performance test does not stop just at finding problems but goes on to give solutions that would uplift and improve the experience of the users. Meticulous planning and sustaining enhancements through cooperation chart a way toward navigating hindrances in testers, which lead to success in software applications. Connect with experts at Clarion to get started.
Author







